Business Beyond Boundaries.
Macanne® is The Only Multi-Platform Agency. Trusted by many since 2012.
Experienced teams and an agile framework, combined with an ever growing passion for creativity we take our clients to futureproof their ventures and deliver the highest business value.
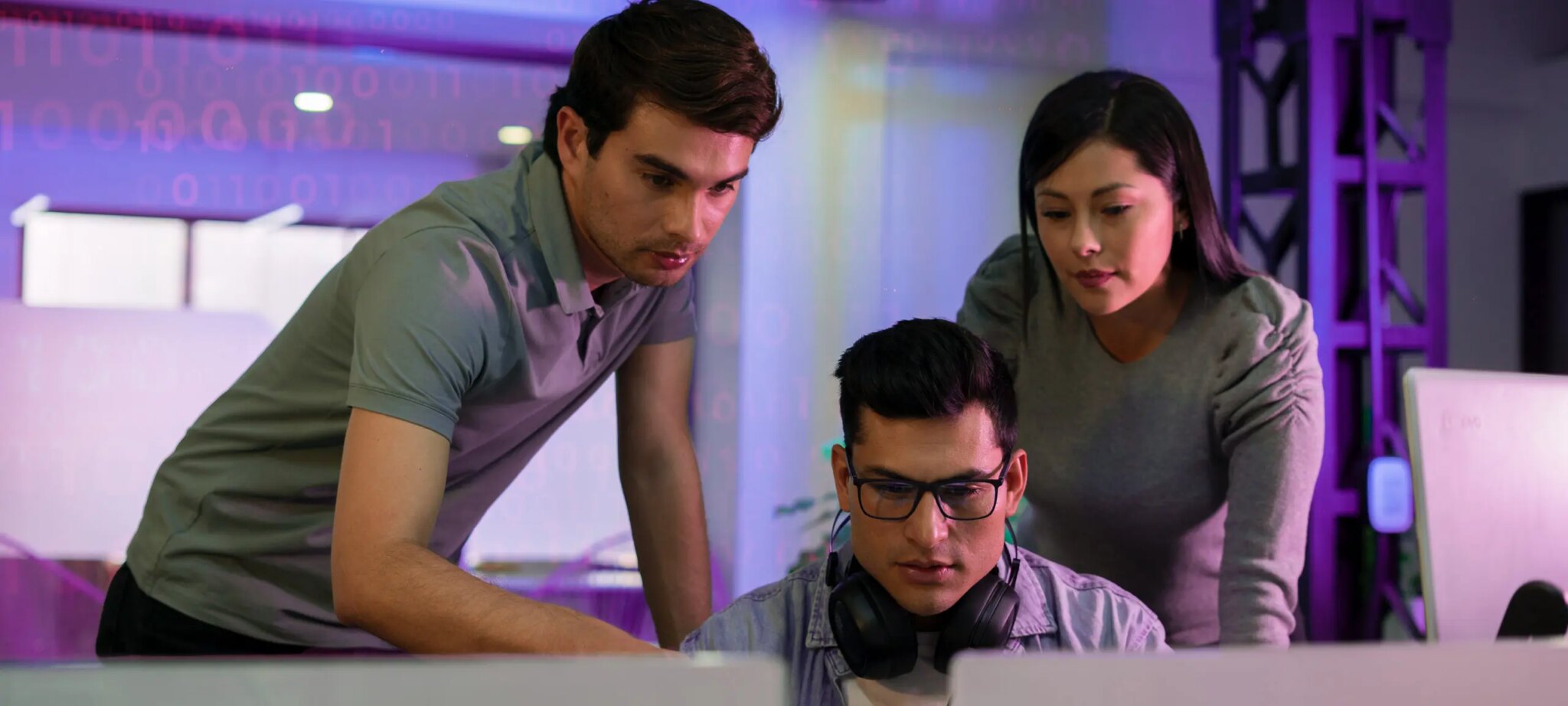







We provide clients
with award-winning services
Our best projects from our caliber team.
Some Industries we’ve excelled in
Digital Marketing
Reach the right customers and get outstanding engagements like no other. Be know, and Be in the know, beyond boundaries
Web Hosting and Development
Maximize your digital presence by entrusting us to host and develop your next website within Macanne’s exclusive ecosystem. No third parties, No Fuss.
Fintech
Fintech projects are strict.
We bring our innovative approach to it.



Organizations recognized our work
Council 2022
Agency
in Ireland 2023
Macanne has been recognized as one of the top agencies in Dublin (2023)
We use latest technologies to run your project smoothly
Get what you need. Pay only for what you use.
Collective Experience
All-time
helped
Globally
Meet Our Team
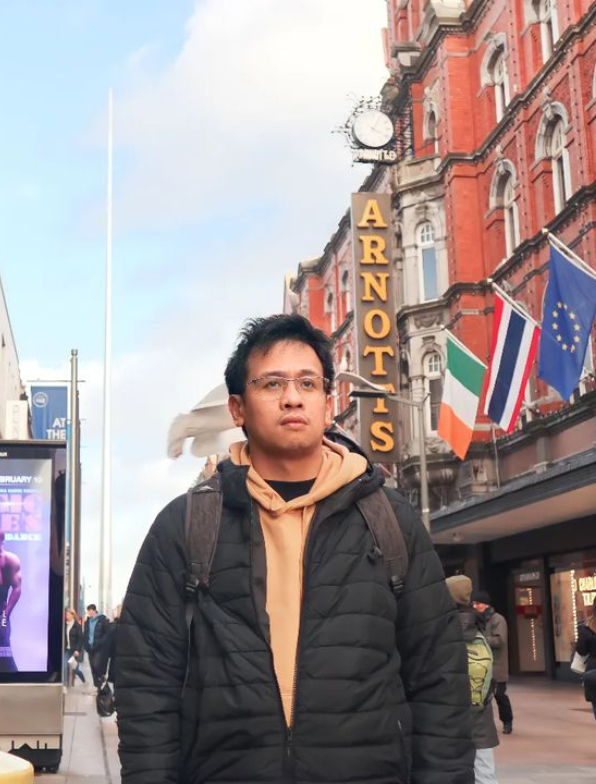

Macky Daus
Co-Founder and Chief Innovations Officer
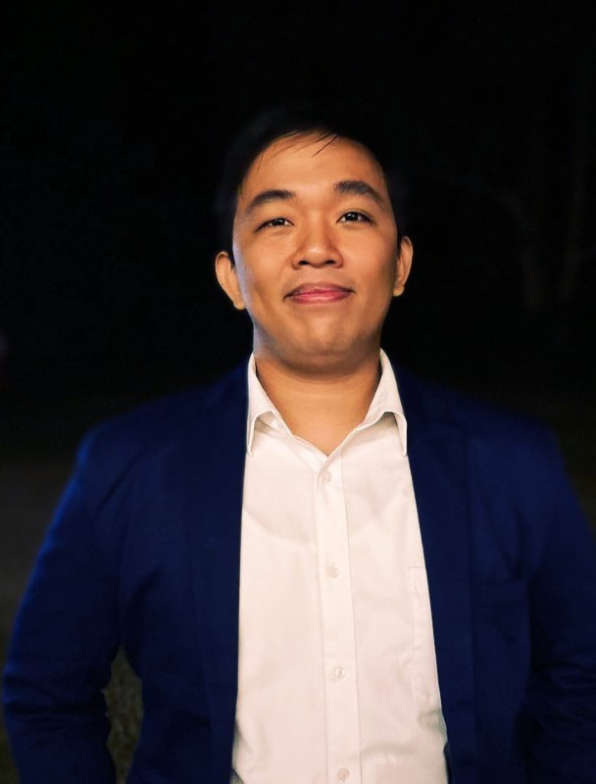

Darren Dario
Co Founder and Cloud Director
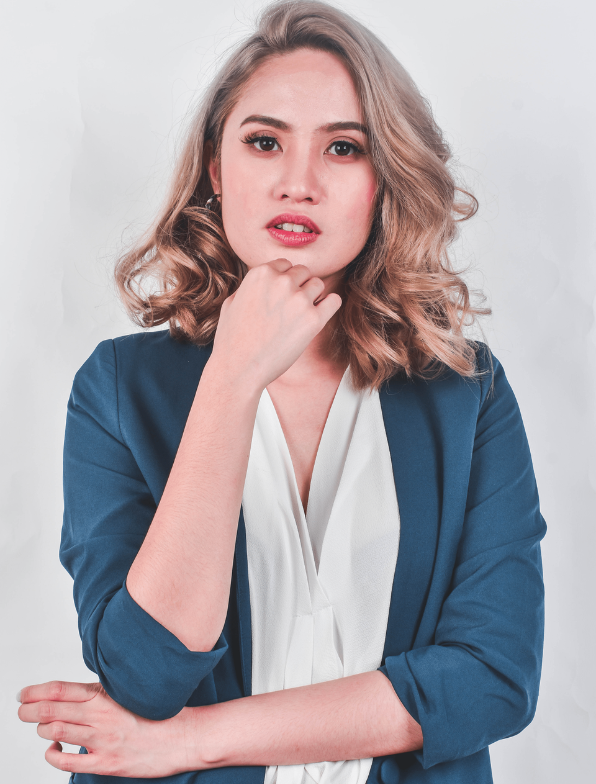

Mich De Joya
Managing Director and Business Operations

Antonette Aquino
Co-Founder and Chief Digital Correspondent

Lauren Connolly
EU Operations Head
Latest Insight
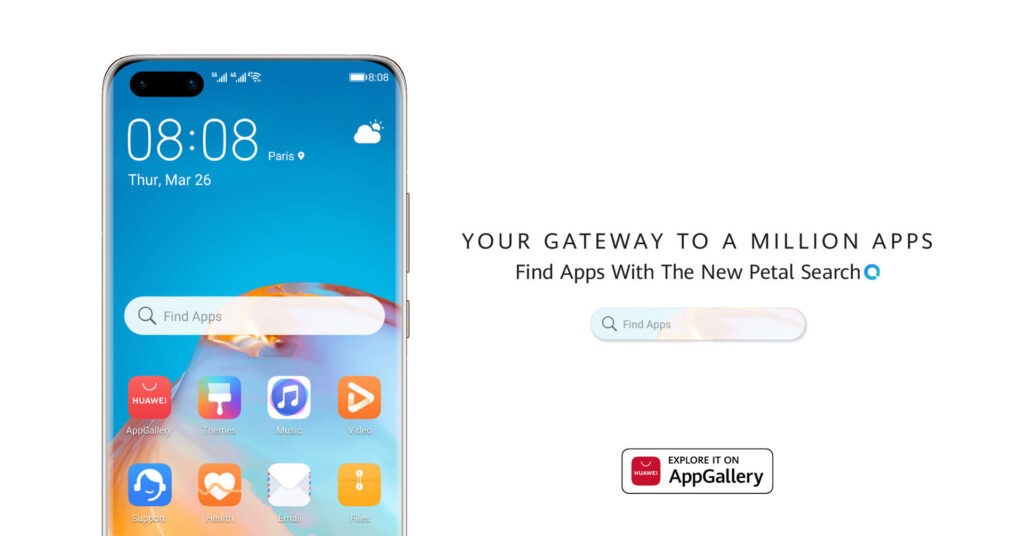
Huawei PetalSearch
Petal Search is one of the key applications in Huawei’s ecosystem. It’s essentially a search engine app developed by Huawei that aims to provide users with comprehensive search results and access to various types of content. Petal Search is designed to help users find information, apps, news, images, videos, and more, directly from their Huawei devices.
✔︎ Digital transformation
✔︎ Consulting services